ASiCC
Project objectives
The objective of the ASiCC project is to develop adaptive SiC-based power electronic converters for multi-terminal medium-voltage direct current (MVDC) distribution grids.
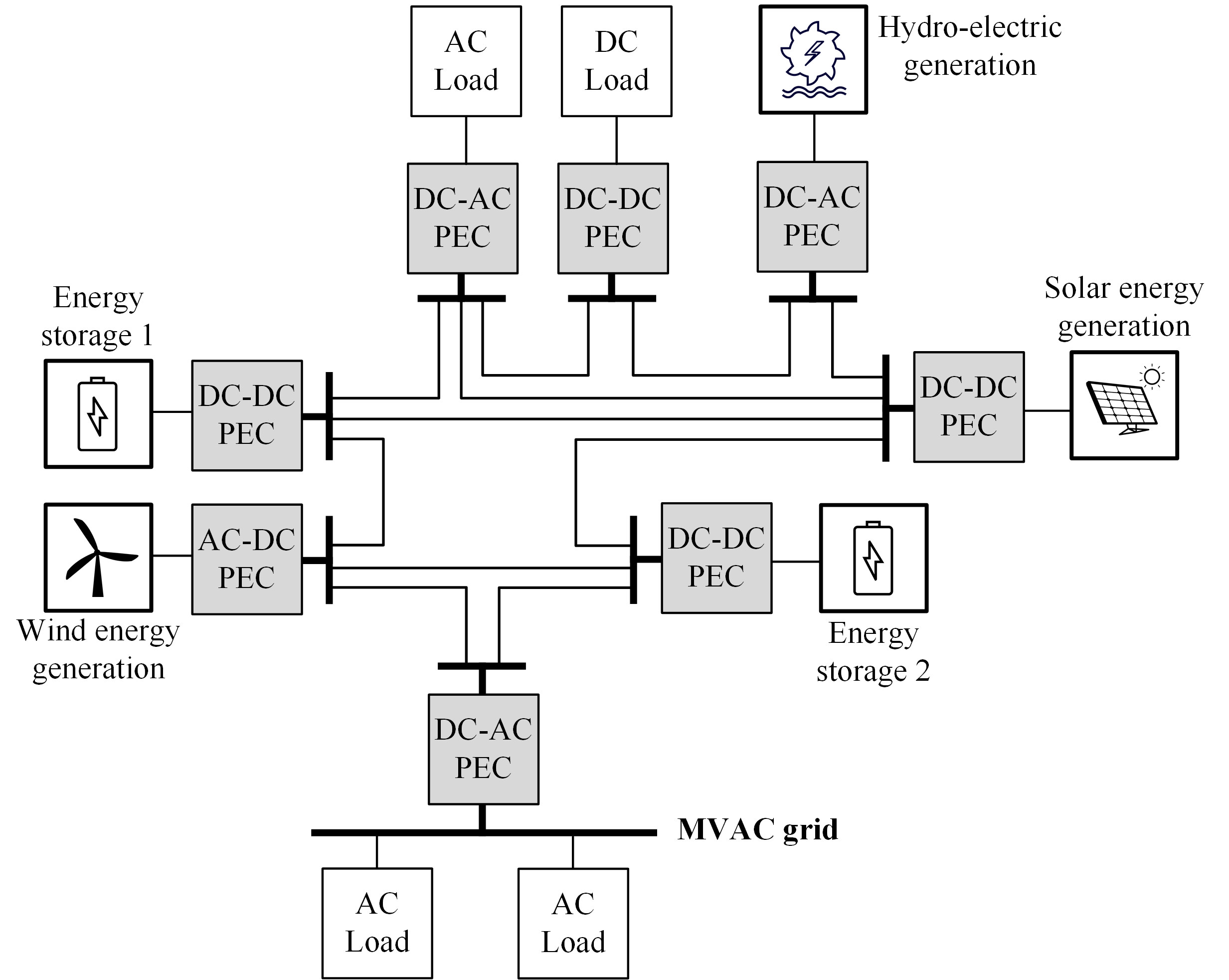 |
Block diagram of a multi-terminal MVDC grid with ring architecture. |
Summary
The urgent societal challenge of decarbonization of the existing electric power grid infrastructure necessitates the integration of more renewable energy sources, which imposes the entire transformation of the existing grid infrastructure towards the future smart grid. The medium-voltage direct current (MVDC) grids are the key technology that will fulfill several design and operating constraints of the future smart grid, such as flexible power control and a more liberal energy market. Power electronics converters (PECs), which are semiconductor-based electrical energy conversion apparatus, will be one of the most vital components of the future MVDC grids. However, the current Silicon-based semiconductor technology has reached its theoretical limits. Exploiting the advantageous characteristics of Silicon Carbide (SiC) technology will enhance the performance of PECs in terms of efficiency, operating temperature and power density. High-voltage SiC is the ideal semiconductor replacement of Silicon in MVDC PECs. Today, PECs have fixed designs and exhibit their maximum performance for a narrow operating range. The key objective of ASiCC is to deliver digitally adaptive PECs designs and operating methodologies by incorporating digital information from load and source variability and semiconductors temperature variations. The novel digitally adaptive PECs designs will dynamically alter their overall electrical, thermal and reliability performance by shaping the switching behavior of the high-voltage SiC semiconductors. The research activities within ASiCC will be implemented by conducting theoretical and simulation studies, as well as, by experimentally validating various digitally-adaptive PECs concepts. At the current stage of the ASiCC project, the design and performance of SiC-based and medium-voltage PECs interfaces for utility scale photovoltaic installations and utility-scale battery storage systems with MVDC grids is investigated. The focus of these investigations is on thermal performance, as well as, on system and semiconductors reliability real-time enhancement. The project team consists of the project manager and two PhD students who will be employed at the Department of Electric Power Engineering at NTNU. Dissemination activities and communication of the research findings with Academia and industry are planned to ensure the highest impact of the proposed research.
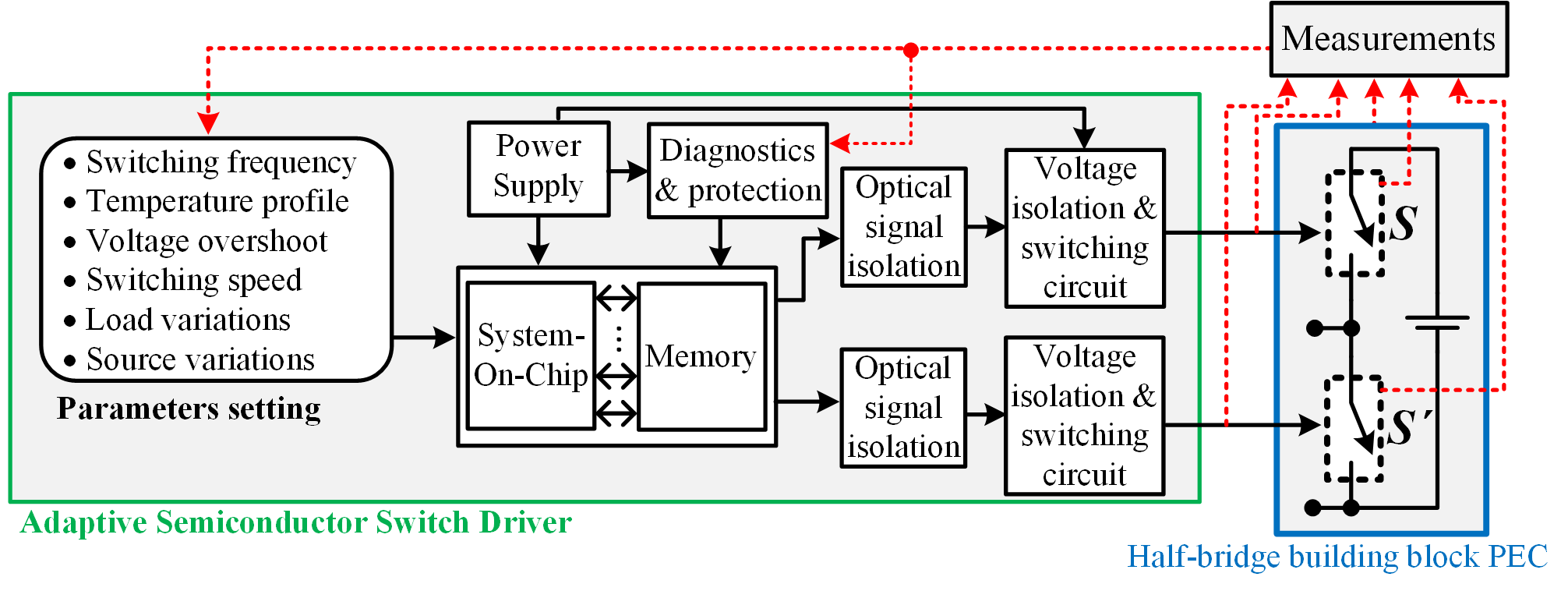 |
Block diagram of the adaptive gate driver for SiC power switches |